

Describe how to create your own sequence databaseġ4. Apply the phylogenetic tool to construct phylogenetic trees and explain the relatedness of bacterial or pathogen strainsġ3. Demonstrate how to construct phylogenetic tree based on SNPsġ2. Explain the concept and be able to use the integrated bacterial analysis pipeline for batch analysis and typing of genomic dataġ1. Utilize the tools for Salmonella and E.coli typing, plasmid replicon detection and plasmid typing in real cases of other bacterial and pathogen genomes.ġ0. Describe the methods behind the tools for Salmonella and E.coli typing, plasmid replicon detection and plasmid typingĩ. Apply the tools for species identification, MLST typing and resistance gene detection in real cases of other bacterial and pathogen genomes.Ĩ. Enumerate the methods behind the tools for species identification, MLST typing and resistance gene detectionħ. Describe how to do de novo assembly from raw reads to contigsĦ. Define the concept of Next-Generation Sequencing and describe the sequencing data from NGSĥ. We offer a very easy to join Reseller program simply fill out a form, and once you're approved, you can start right away. Apply genomic tools for sub-typing and surveillanceĤ. We offer flexible partnership that suits your selling style so your company can offer TypingMaster 11 to your clients or you can receive leads from us. Give examples of the applications of Whole Genome Sequencing to Surveillance of bacterial pathogens and antimicrobial resistanceģ. If this is your first time with touch typing, then you might spend a lot of time. Describe the general Principles in typing of BacteriaĢ. However, the quickest way to master typing will be learning touch typing. īy the end of this course you should be able to:ġ. It will also give the opportunity to learners to learn about online tools and what they can be used for through demonstrations on how to use some of these tools and exercises to be solved by learners with use of freely available WGS analysis tools.
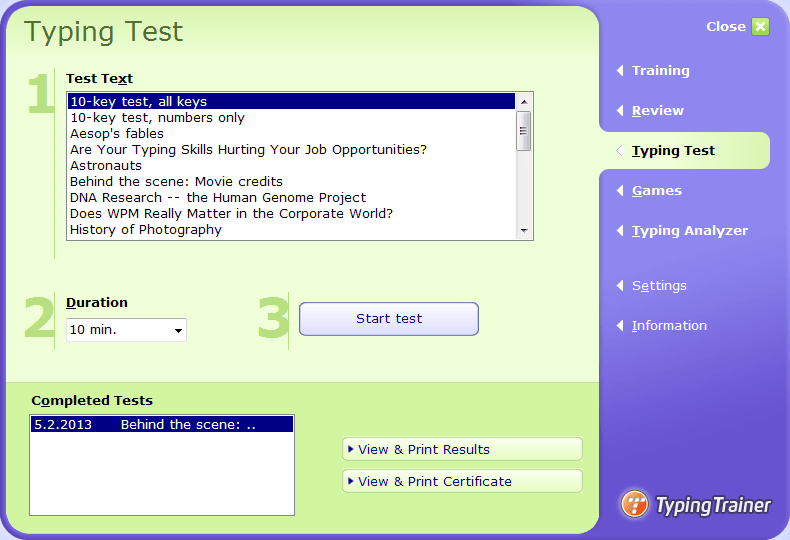
The course will give the learners a basis to understand and be acquainted with WGS applications in surveillance of bacteria including species identification, typing and characterization of antimicrobial resistance and virulence traits as well as plasmid characterization.

WGS technology and applications are high on international political agenda, as the classical methods are being replaced by WGS technology and therefore bioinformatic tools are extremely important for allowing the people working in this sector to be able to analyze the data and obtain results that can be interpreted and used for different purposes. This course will cover the topic of Whole genome sequencing (WGS) of bacterial genomes which is becoming more and more relevant for the medical sector.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
